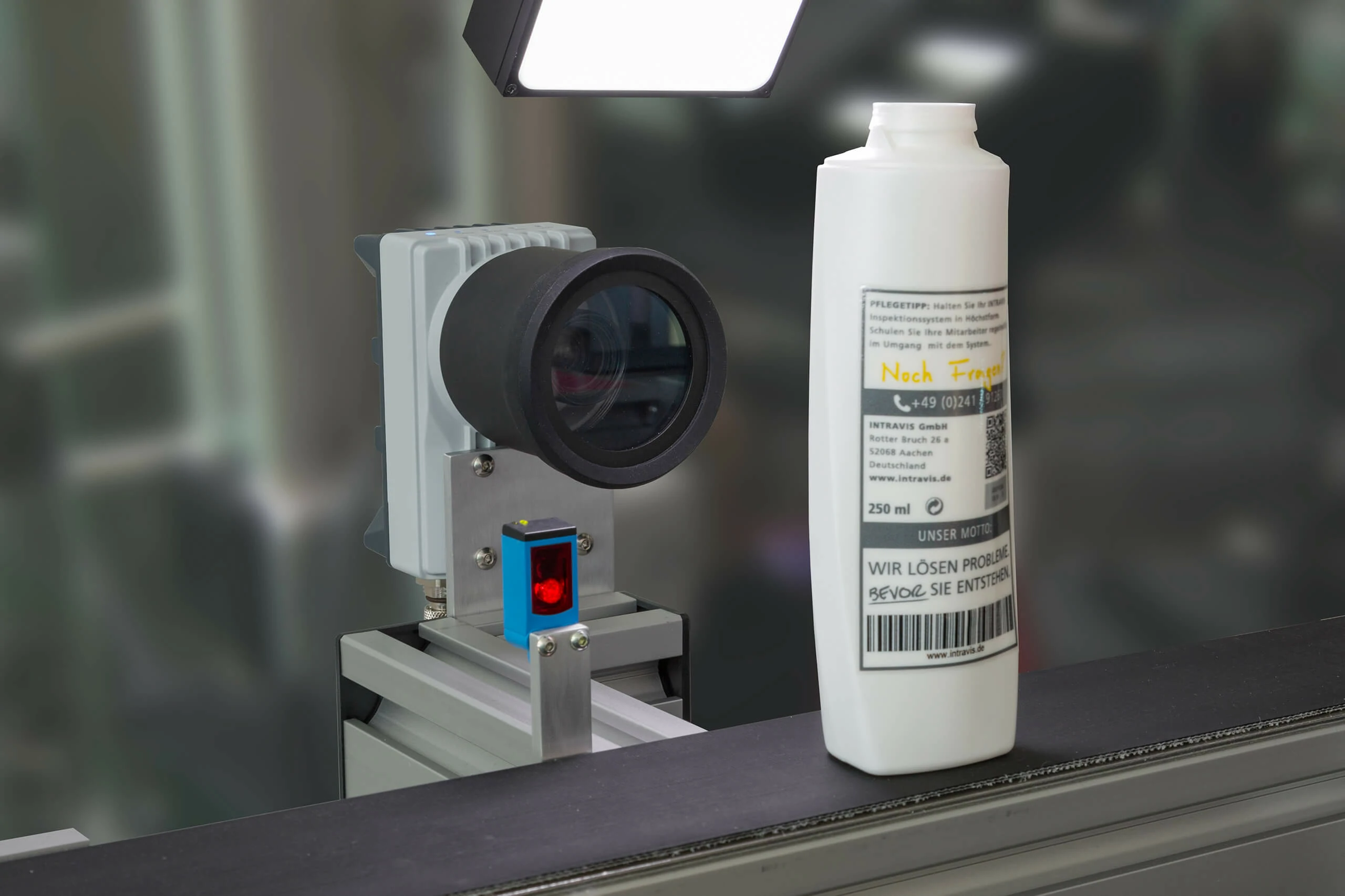
Food labeling occupies a central role in the food production process because it communicates product details to consumers and meets government regulations. Food manufacturers must ensure that each label conveys clear information about ingredients, allergens, expiration dates, and nutritional facts. In this article, manufacturers will gain insights into the structured process of food labeling and the impact of modern automated machines on packaging operations.
Fundamentals of Food Labeling
Food labeling must meet strict government standards, these include bread food, sweet snack food, salty snack food and so on. Every food company is required to provide accurate nutritional information, list potential allergens, and display clear expiration dates. These requirements are enforced by agencies that set the standards and the associated guidelines.
Components of a Food Label
Food labels contain many key features that serve different purposes. These include:
- Product Identity: Every label must state the product name, enabling consumers to quickly identify what they are buying.
- Nutritional Information: The labels must list calorie counts, fats, sugars, proteins, and other nutrient details.
- Ingredient List: A thorough breakdown of all components is provided. This list helps consumers manage allergies and understand the product’s contents.
- Allergen Information: All companies are required to list any common allergens. Transparency in allergen listing is important for both regulatory compliance and customer safety.
- Expiration Date and Storage Instructions: The label must indicate the best-by or expiration date and any necessary guidance on storage to preserve the product’s quality.
- Barcode and Tracking Data: Modern labels often include codes that allow for efficient tracking and quality control through each step of the supply chain.
The Purpose and Impact of Food Labels
Companies use labels not only for compliance but also for building brand identity and trust. Every consumer makes purchase decisions based on the information presented on the label. Labels are the first line of communication between the brand and the consumer. A clearly printed label that is rich in details creates transparency. In turn, consumers gain trust, and the brand is seen as honest and reliable. With accurate and informative labels, businesses reduce the risks of miscommunication and legal issues.

Automated Labeling Machines: Enhancing Food Labeling Efficiency
Modern food manufacturers are increasingly turning to automated labeling machines to streamline operations. Every automated system is designed to reduce human error, improve production speed, and ensure that every product is labeled uniformly. These machines have revolutionized the packaging industry by supporting high-speed production lines and providing consistent quality.
Advantages of Automation
Automated labeling systems provide a range of advantages for food manufacturers. The efficiency gains from automation are significant and translate into reduced labor costs and minimized waste. Every company that automates its labeling process can expect fewer errors and faster throughput when compared with manual methods.
- Advantages in Detail:
- Consistent Accuracy: Automated systems use sensor technology and pre-programmed guidelines to ensure that labels are placed uniformly. Every label is applied with precision, and every product meets quality standards.
- Reduced Waste: Every process that limits human errors contributes directly to waste reduction. Automated machines minimize the risk of incorrect labeling, which helps save time and resources.
- Improved Production Speed: Every automated labeler is engineered to operate at high speeds, keeping pace with modern production demands. Companies can produce more units in less time without compromising quality.
- Labor Cost Reduction: Every labeling machine is designed to perform repetitive tasks that would otherwise require human intervention. This design frees up staff to focus on quality control and innovation.
Types of Food Labeling Machines
Food manufacturers have several options when selecting an automated labeling machine. Every machine has unique attributes, and companies must evaluate their needs carefully before investing in technology. The principal types of labeling machines include:
Semi-Automatic Labelers
Semi-automatic labeler is best suited for smaller operations or seasonal products. Every operator on these machines handles tasks like loading labels and occasional adjustments.
Fully Automatic Labelers
Fully automatic labeler is ideal for high-volume production lines. Every system uses sensors and software to place labels without human assistance. Every machine works continuously and ensures that every product receives a label accurately.
| Labeling Machine Type | Manual Involvement | Flexibility | Best For | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic Labelers | Partial | Moderate | Small operations, seasonal products | Cost-effective, minimal automation transition |
| Fully Automatic Labelers | Minimal | High | High-volume production lines | Unparalleled speed, consistency, and reduced supervision |

Key Considerations for Choosing Labeling Equipment
Food manufacturers must consider several factors when choosing the right labeling machine for their operation. Every decision must take into account the current workflow, the scale of production, and future business objectives.
Production Volume
Every labeling machine is designed to handle a specific production volume. Companies must carefully evaluate their current output and project future growth. The wrong decision may lead to either an oversupply of capacity, resulting in unnecessary expenses, or an undersupply that slows down production.
- Important Aspects to Evaluate:
- Current output and projected growth.
- The frequency of production runs and potential seasonal fluctuations.
- The scalability options available with the machine model.
Container Diversity
Every food production line may use packaging of different shapes and sizes. Companies must choose a labeling machine that is versatile enough to handle various container forms. Machines that require frequent reconfiguration disrupt workflow and can lead to inconsistencies in labeling.
- What Manufacturers Must Assess:
- The size and shape of the packaging used in the production line.
- The ease with which the machine can adjust to different container formats.
- The machine’s adaptability to accommodate innovative packaging designs.
Labeling Requirements
Every company must prioritize precision in the labeling process. Manufacturers must clearly define their specific needs in terms of speed, precision, and regulatory compliance. The chosen machine must incorporate sensor technology and advanced features that assure each label is applied flawlessly.
- Criteria for Evaluating Labeling Requirements:
- The need for high-speed operation without compromising quality.
- The importance of precision in label positioning and content accuracy.
- The integration of features that support compliance with food labeling standards.
Manufacturers must perform a thorough assessment of these factors in order to select a labeling machine that not only matches their current requirements but also adapts to future demands. Every choice influences productivity and can determine the long-term success of the packaging operations.
Quick Reference Table for Labeling Machine Selection
| Factor | Consideration | Action Item |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Determine if your production is seasonal or continuous. | Evaluate current output and forecast future demand. |
| Container Compatibility | Ensure that the machine can handle various container shapes and sizes. | Test machine compatibility with sample products. |
| Precision Requirements | Assess the need for high-precision sensors and error-checking features. | Review machine specifications for alignment technology. |
| Maintenance Needs | Confirm the availability of maintenance and upgrade options. | Schedule maintenance and training with vendor support. |
| Cost and ROI | Consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial price. | Perform a cost-benefit analysis and ROI estimation. |
Integrating Food Labeling Machines into Production Lines
Every integration project must address both the hardware and software aspects of a production line. Companies that seamlessly incorporate automated labeling systems into their workflows can expect significant improvements in productivity and quality.
Planning the Integration Process
Every company must plan carefully when integrating new machines. Detailed mapping of the production line is essential. Companies must design integration strategies that minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition from manual to automated processes.
- Key Steps in Integration Planning:
- Assess Existing Workflows: Every company must evaluate its current production procedures and identify bottlenecks.
- Define Objectives: Every integration project must include clear targets such as error reduction, speed enhancement, and regulatory compliance.
- Plan for Staff Training: Every employee must receive proper training to operate the new equipment.
- Implement a Pilot Phase: Every manufacturer should run a pilot project before full-scale integration to identify potential issues early on.
Benefits of Seamless Integration
Every advantage of automation is amplified when machines are integrated effectively. Companies that manage the integration process well experience fewer disruptions and significantly improved consistency in the labeling process.
- Integration Advantages Include:
- Streamlined production processes that contribute to overall cost reduction.
- Improved data collection and real-time monitoring of labeling quality.
- Enhanced workflow coordination that supports high-speed production and regulatory precision.
Every successful integration reinforces the importance of planning, collaboration, and continuous improvement in production operations.
Conclusion
Food labelling and packaging is an important part of food production. By adopting automated labeling machines, companies can expect to increase production speed, reduce errors, and improve overall product quality.
The following table summarizes recommendations for integrating food labeling machines into production lines:
| Aspect | Key Considerations | Benefits | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance | Adherence to labeling laws, nutrition data, allergen warnings | Avoids fines and recalls, fosters trust | Regular reviews and automated updates |
| Production Volume | Matching machine capacity with current and future output | Cost-efficiency and scalability | Analyze KPIs and project growth trends |
| Container Compatibility | Versatile handling of diverse shapes and sizes | Reduces downtime and boosts operational flexibility | Choose equipment with easy reconfiguration options |
| Automated Accuracy | Integration of sensor technology, precision label placement | Uniform labeling and reduced product waste | Monitor machine performance and schedule quality checks |
| Modular Systems | Flexibility for upgrades and changes in product lines | Future-proofing operations and simplified scaling | Implement incremental upgrades and training programs |
Autmachine continues to lead the way by offering customizable food labeling machines that seamlessly integrate into existing food production lines to maximize efficiency. Every production facility should consider the long-term benefits of adopting modern automated systems and modular packaging solutions.
For a tailored labeling solution that fits your unique production needs, contact us at jinlian@autmachine.com or penny@autmachine.com.

FAQ
A food labeling machine is an automated or semi-automated device used to apply labels to food packaging. Investing in a labeling machine helps businesses meet regulatory standards, improve production speed, and maintain consistent branding across products.
Choosing the right labeler depends on three main factors: your production volume, the type of packaging containers you use, and the labeling requirements (such as speed or precision). For low-volume operations, a semi-automatic labeler may suffice. For high-speed production, a fully automatic is more suitable.
Absolutely. Many modern machines are designed to handle a wide range of shapes and sizes—bottles, jars, pouches, boxes, and more.